15 More of the Most Recent Space Discoveries from 2025

2025 has been a massive year for NASA and all astronomers. Earth doesn’t have a formal “astronomy division,” but with all collaborations between space-scouring teams across the globe, it basically does. If we were scoping things out in the Northern Hemisphere, we’d wanna know what the folks down south were seeing!
As outsiders looking in (instead of insiders looking out), all we can do is imagine scoping things out like the pros. Best we can do for now is relay the wonders they’re observing, and the stuff they’re figuring out because of it. So here’s the most recent batch of space goodies discovered in 2025.
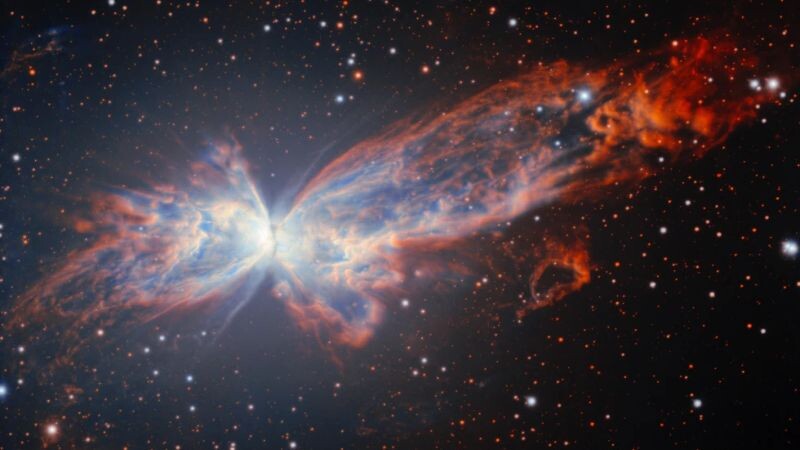
The Butterfly Nebula

NSF NOIRLab
This photo of the Butterfly Nebula (NGC 6302) was released on November 26, 2025. It is a bipolar planetary nebula in the constellation Scorpius (about 3,400 light-years away) and was formed by a dying star that created two large, energetic "wings" of gas. Its central star is one of the hottest known, with a temperature of 220,000 Kelvin.
The “Infinity” Galaxy
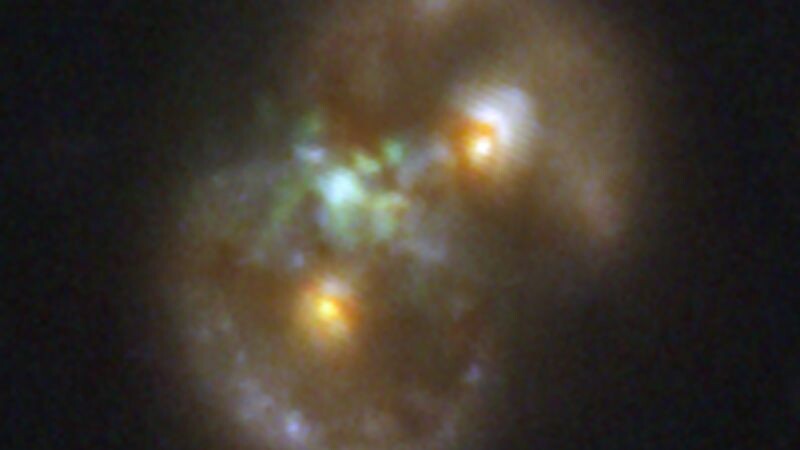
Wikipedia
Recently identified in the James Webb Space Telescope’s COSMOS-Web survey, it was discovered by researchers from Yale and the University of Copenhagen. It was likely formed from the merger of two disk galaxies, and astronomers believe it’s the first-of-its-kind view of a supermassive black hole being born.
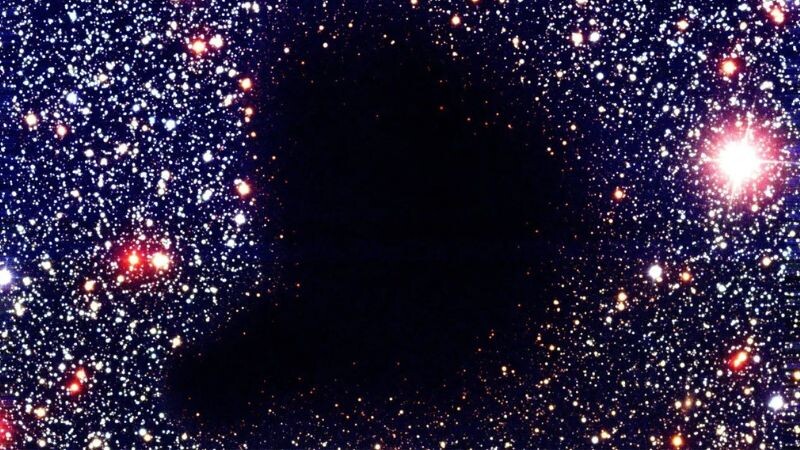
New theories about The Boötes Void

YouTube
Also known as “The Great Nothing,” this enormous seemingly blank region is almost 330 million light-years in diameter (representing approximately 0.27% of the diameter of the observable Universe). It was discovered by Robert Kirshner and his team in 1981, but with better images of it than ever, several new theories about the void have recently emerged.
Scientists may have "seen" dark matter
An article published on Nov 29, 2025 reports that scientists may have "seen" dark matter for the first time. A recent study of a strange gamma-ray emission from the center of the Milky Way marks a significant moment in the search for this mysterious, invisible substance that makes up about 85% of the universe's matter.
We now know exactly what supernovas look like

Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScl
After the James Webb Telescope discovered a supernova known as SN2025pht on June 29, 2025. Charlie Kilpatrick of Northwestern University said, “Only now, with JWST, do we finally have the quality of data and infrared observations that allow us to say precisely the exact type of red supergiant that exploded and what its immediate environment looked like.”
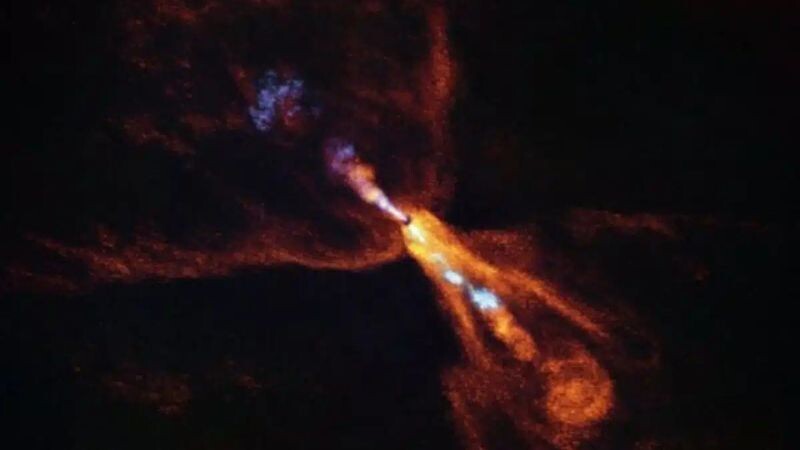
Astronomers witnessed the birth of a new solar system

ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO)
In July 2025, using the James Webb Space Telescope and ALMA telescope in Chile, teams have captured an image of a new solar system forming around a young star called HOPS-315 (about 1,300 light-years away). This offers a real-time look at the initial steps of planet formation, similar to our own solar system's origins.
They may have located some of the first stars in the universe
According to a study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on Oct. 27, 2025, astronomers believe they have discovered “Population III stars” — which are the universe’s first generation of stars that formed shortly after the Big Bang. Researchers argue that this is the first cluster to satisfy all the major theoretical predictions about the earliest stars.
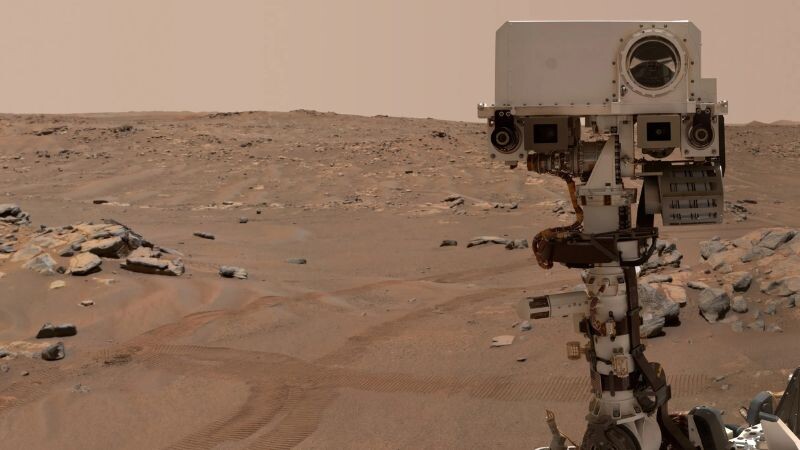
The strongest evidence of life on Mars

NASA/jpl-caltech/msss
In September 2025, NASA's Perseverance Rover found a Martian rock with patterns called "leopard spots" and "poppy seeds," which are potential signs of ancient microbial life. Scientists emphasize this is not definitive proof of life but is considered the strongest hint yet, and further study of the rock samples on Earth is needed for confirmation.
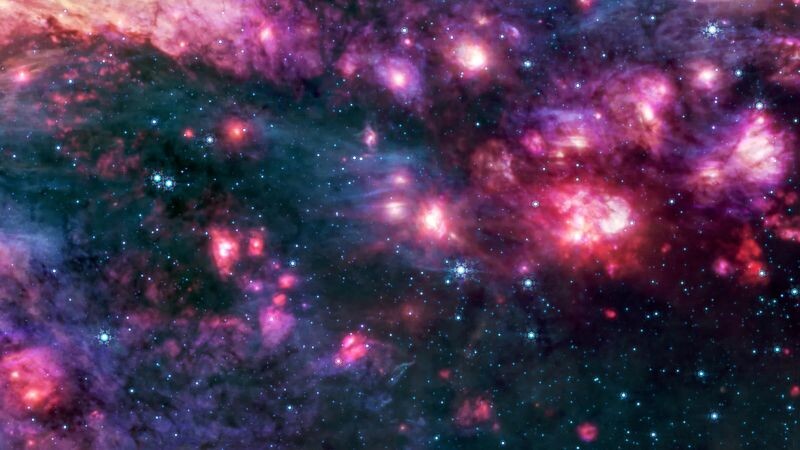
The Sagittarius B2 Molecular Cloud

NASA (Image Processing Alyssa Pagan - STScI)
On Sept. 24, 2025, the James Webb Telescope captured glowing cosmic dust heated by very young massive stars in unprecedented detail. Sgr B2 is the most massive and active star-forming region in our galaxy, located only a few hundred light years from our central supermassive black hole.
A moon-forming disk around a planet
The James Webb Telescope found a carbon-rich disk surrounding the planet CT Cha b (located 625 light-years away). Results published on September 29, 2025, state that it’s a possible construction yard for moons.
The Cat’s Paw Nebula
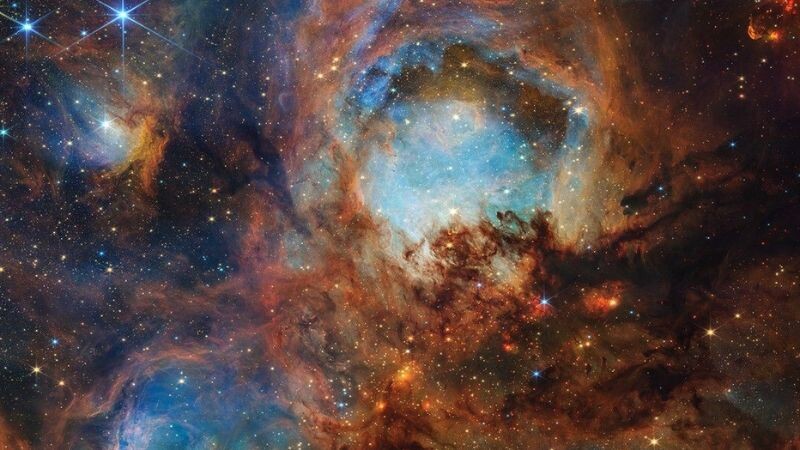

Image: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI
While less-clear images of it have been captured by NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer telescopes, the James Webb telescope recently revealed a subset of mini structures composed of gas, dust, and young stars. This Nebula is located approximately 4,000 light-years away in the constellation Scorpius.
The effect of atmosphere on a planet’s daytime temperature
With evidence found on September 30, 2025, researchers can now determine whether or not a tidally locked rocky planet has an atmosphere by comparing its measured temperature to computer models.
An mid-infrared image found four serpentine spirals
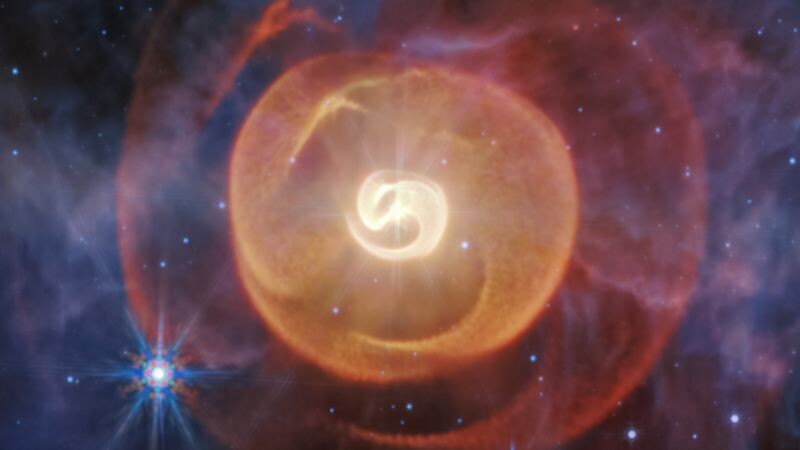

NASA (Image Processing Alyssa Pagan - STScI)
Where previous observations only showed one, the James Webb Telescope recently found four dust spirals. Webb’s data also confirmed that three stars in the image are gravitationally bound to one another. These spirals or “shells” were emitted over the last 700 years by two aging Wolf-Rayet stars in a system known as Apep (a nod to the Egyptian god of chaos).
A possible Earth-like planet
In September, 2025, NASA observed seven Earth-sized worlds orbiting the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1. Planet e is of particular interest because it orbits the star at a distance where water on the surface is theoretically possible, but only if the planet has an atmosphere.
A massive protostellar jet
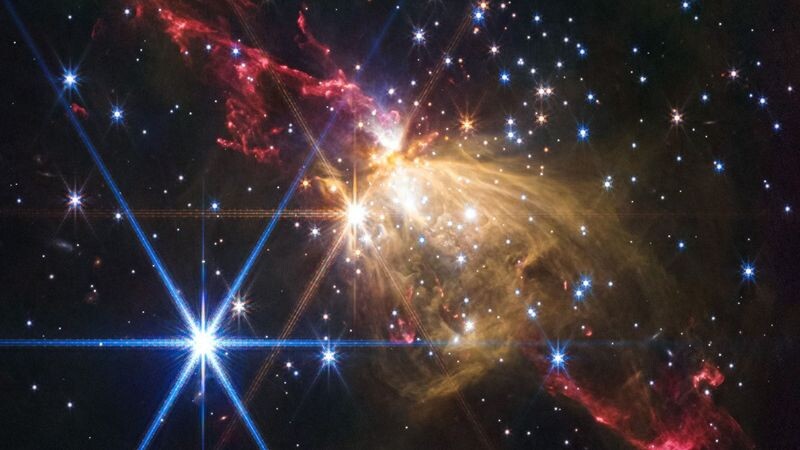

NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Yu Cheng (NAOJ)
A “protostellar jet” is a fast-moving stream of gas ejected from the inner disk of a young stellar object during star formation. This one in Sh2-284, found on the outskirts of our Milky Way, is roughly 8 light-years long. For scale, one light-year is equal to about 5.88 trillion miles.